Deep vein thrombosis or DVT is a blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the legs. This condition is serious because blood clots can travel and spread to the lungs. Leg pain or swelling, redness are the most common symptoms.
Causes
Although DVT mostly affects the elderly, it can happen at any age, especially if you are prone to health-related risk factors. You’re at greater risk of developing a deep-vein blood clot if you’re obese, have a family history of DVT, had pregnancy complications, sit for long periods of time, pulmonary embolisms, or clotting disorders.
Symptoms:
- Swelling in leg
- Pain or tenderness in calf, foot, or leg
- Warm skin in extremities
When should you consult a doctor?
Visit a doctor right away if you have any of the symptoms, especially if they appear suddenly: Swelling in one or both legs, pain or tenderness in your leg, ankle, foot, or arm. About one in 10 people with an untreated DVT develop a severe pulmonary embolism so an early detection can avoid complications and fatality.
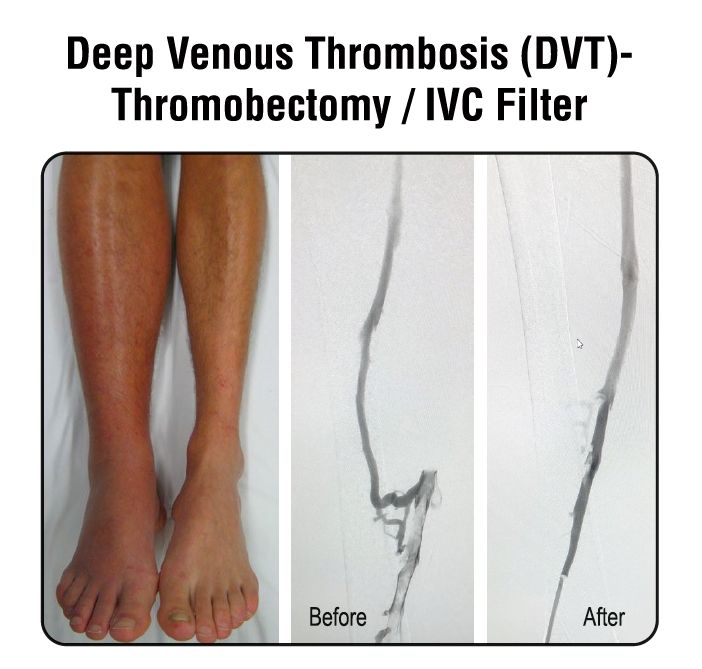
Our Treatment
There are three main goals of a DVT treatment.
- Prevent the clot from getting bigger.
- Prevent the clot from breaking loose and spreading to the lungs.
- Reduce your chances of repetition
At Ruge Vascular Center we analyse your symptons, conduct physical exams to check for areas of swelling, tenderness, and changes in color of skin. Based on the findings we proceed with treating the symptons by applying predominantly two methods
1. Thrombolysis
Thrombolysis, also called fibrinolytic therapy, is the breakdown (lysis) of blood clots formed in blood vessels, using medication.
2. IVC Filter
The IVC filter is placed through a small incision in the inferior vena cava. This filter prevents large clots from going into the pulmonary system thereby avoiding pulmonary embolism.
